The next guide in the VPN Split Tunnel sequence is the Install Transmission BitTorrent Client for VPN Split Tunneling on Ubuntu 16.04 and Debian 8, Minibian and Raspbian Jessie (on Raspberry Pi).
The next guide in the VPN Split Tunnel sequence is the Install Transmission BitTorrent Client for VPN Split Tunneling on Ubuntu 16.04 and Debian 8, Minibian and Raspbian Jessie (on Raspberry Pi).
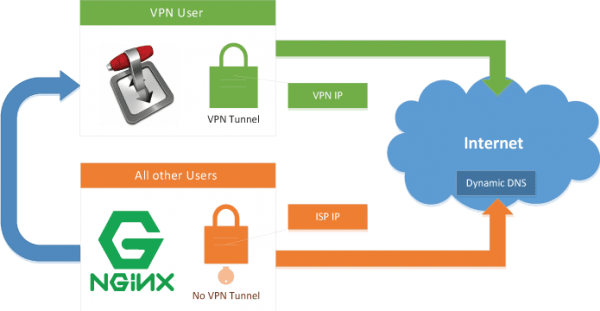
It is highly recommended to run your BitTorrent client over VPN to protect your online privacy, and one of the best ways to do this is by using VPN Split Tunnel where only Transmission's traffic will be routed over VPN connection and you will retain your direct connection to Internet for all the other users. This method also implements the Automatic Kill Switch option and prevents possible DNS leaks. To access Transmission you will need nginx Reverse Proxy (even on local network).
| VPN Service | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Private Internet Access | ($3.33 / month) | |||
| Pure VPN | ($4.91 / month) | |||
| IPVanish | ($6.41 / month) |
Configure Transmission for VPN Split Tunnel on Ubuntu 16.04 and Debian 8 (including Minibian)
Part 1 is to complete the guide Force Torrent Traffic through VPN Split Tunnel Debian 8 + Ubuntu 16.04. If you have already configured Split Tunnel, then you can continue with this Part 2 guide to configure Transmission to use the VPN split tunnel. It is important that you have a working Split Tunnel on your server before you can proceed with configuring Transmission for VPN Split Tunneling, otherwise it will not work!
Installation Overview
- Install Transmission
- Configure Transmission to use the VPN split tunnel
- Verify Transmission is using the VPN
- Configure the nginx reverse proxy to keep remote access of Transmission
Important: This guide is written for Ubuntu Server 16.04 LTS and Debian 8 systems (like Minibian, Raspbian, Bananian) that uses systemd services. It might work on other Linux distributions, but it is guaranteed to work on Ubuntu Server 16.04 LTS and Debian 8. For Ubuntu Server 14.04 LTS, upstart scripts are required instead of systemd services. If you are using Ubuntu Server 14.04 LTS, jump to the Configure Transmission for VPN Split Tunneling on Ubuntu 14.x guide.
Install Transmission BitTorrent Client Ubuntu 16.04 LTS
After configuring the VPN Split Tunnel in Part 1, we need to install Transmission and configure it to run as the vpn user so that only the Transmission torrent traffic goes through the VPN connection. In case of Ubuntu Server 16.04 we will use the official Transmission PPA to make sure the latest Transmission version is installed.
Note: If you are on Debian 8 (Minibian, Raspbian) then skip this part and go to the Debian 8 section of this guide.
Add the Transmission Ubuntu repository
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:transmissionbt/ppaUpdate packages and install Transmission
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install transmission-daemon -yTransmission is now installed, you can proceed to the Create Systemd Service Unit part of the guide.
Install Transmission BitTorrent Client Debian 8 (Minibian, Raspbian)
After Part 1 of the Split Tunnel VPN guide is completed, and you have a working VPN Split Tunnel configured on your system, it is time to install Transmission.
On Debian 8 (Minibian, Raspbian) it is simple as the following
apt-get update
apt-get install transmission-daemon -yCreate Systemd Service Unit
First we need to modify the systemd service for transmission-daemon to run as the vpn user.
Stop the Transmission service
sudo systemctl stop transmission-daemonNext we will override the default systemd unit by creating a drop-in snippet which is applied on top of the original unit. It is the proper way to edit systemd unit files provided by packages. If Transmission is updated, the changes will remain and not be overwritten.
Note: on Minibian you don't need to use sudo
Create the required folder and conf file
sudo mkdir -p /etc/systemd/system/transmission-daemon.service.d
sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/transmission-daemon.service.d/local.conf
Copy and paste the following content. This will ensure Transmission is run as vpn user, and that the Transmission service is started after the VPN tunnel (tun0) is up.
[Unit]
After=sys-devices-virtual-net-tun0.device
Wants=sys-devices-virtual-net-tun0.device
[Service]
User=
User=vpn
Group=
Group=vpn
Type=simple
ExecStart=
ExecStart=/usr/bin/transmission-daemon -f --log-error -g /etc/transmission-daemon
Restart=on-failure
RestartSec=10Ctrl+X, Y and Enter to Save.
Finally, reload systemd to scan for new and changed units
sudo systemctl daemon-reloadConfigure Transmission for VPN Split Tunnel
We are going to run Transmission as vpn user, therefore we need to change the ownership of the Transmission configuration files
sudo chown -R vpn:vpn /etc/transmission-daemon/sudo chown -R vpn:vpn /var/lib/transmission-daemon/
Give the Transmission settings file write and execute permissions for the vpn user and group.
sudo chmod -R 775 /etc/transmission-daemon/sudo chmod -R 775 /var/lib/transmission-daemon/
I strongly recommend to create a download folder for your torrents and set the required permissions. In this example we will create a folder Downloads in the regular user's home directory, in our case it is htpcguides. Of course, you should modify the path to fit your setup replacing htpcguides with your username.
Create the download folder if it doesn't already exist
mkdir /home/htpcguides/DownloadNow set the permissions of your download folders
sudo chown -R vpn:vpn /home/htpcguides/Download
sudo chmod -R 775 /home/htpcguides/DownloadThe rpc-whitelist setting specifies which IP addresses may access the Web interface. We are going to use an nginx reverse proxy to retain remote access to the Transmission web interface. With this method it is sufficient to limit access to the localhost only – the default value. This will work just fine as long as Transmission and nginx are running on the same server. In addition, it is much more secure since only localhost will have access to Transmission.
Note: since we limit access to Transmission except the localhost (using iptables from the Part 1 of the guide), you can not access Transmission GUI even if you whitelist your home network range. You need to use nginx reverse proxy.
Open up the Transmission configuration file for editing
sudo nano /etc/transmission-daemon/settings.jsonChange the remote access username and password to your liking
"rpc-password": "password",
"rpc-username": "username",Change the download directory to where you want to store your torrent downloads. By default it is /var/lib/transmission-daemon/downloads/ but if you created a new directory like described few lines before, make sure you enter that path.
"download-dir": "/home/htpcguides/Download",Set umask to 002 to avoid permission issues, these are equal to 775
"umask": 002,Ctrl+X, Y and enter to save.
Now you should start Transmission
sudo systemctl start transmission-daemon.serviceConfigure Transmission Remote Access with nginx Reverse Proxy
At this point you should have a fully working VPN with Split Tunneling and a running Transmission client tunneled over the VPN connection. To access Transmission Web UI with a split tunnel you need to create a reverse proxy.
The following section will show you how to configure nginx reverse proxy. Note this configuration uses plain, unencrypted http connection for nginx. If you plan to access Transmission from outside of your local network you should consider configuring nginx with a secure SSL certificate using our guide Secure nginx Reverse Proxy with Let’s Encrypt, or alternatively you can configure with a self-signed certificate following the guide Enforce SSL for Secure nginx Reverse Proxy Linux (now that Let's Encrypt provides free valid certificates, I strongly recommend to use it).
If you need access to Transmission (or other services) only from your local network, then you can use the following simple nginx configuration.
Install nginx
sudo apt-get install nginx -yCreate a new nginx site
sudo nano /etc/nginx/sites-available/reverseAdd these lines, adjust your dynamic DNS address (mine is htpcguides.crabdance.com) and local IP address (mine is 192.168.40.100). If you changed your default Transmission port change 127.0.0.1:9091 to reflect your port. If you already have a reverse proxy virtual host configured then you only need to add the blue section.
Note that the red curly bracket closes the server block so if you add more reverse proxies you will have to do so before the second curly bracket.
server {
listen 80;
server_name htpcguides.crabdance.com, 192.168.40.100;
location /transmission {
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:9091;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
}
}Ctrl+X, Y and Enter to Save and exit
Disable the default nginx site
sudo unlink /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/defaultEnable the reverse proxy site with Transmission enabled
sudo ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/reverse /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/reverseRestart the nginx service
sudo service nginx restartRestart the transmission-daemon
sudo systemctl restart transmission-daemon.serviceYou can now access Transmission using the reverse proxy at http://ip.address/transmission or using your dynamic DNS address http://yourdns.address/transmission (Remember, you can access Transmission only through the nginx reverse proxy).
To access it outside the home network you will need to forward port 80 or in your router to the machine hosting nginx but beware of security risks like brute force attacks (guide). You can use the local IP address from within your home network, but when accessing it outside the home network you need to use the dynamic DNS address. As already mentioned, if you want to access nginx from outside of your local network, don't use plain, unencrypted http connection, but configure a secure TLS/SSL nginx configuration by following the guide Secure nginx Reverse Proxy with Let’s Encrypt
Recommended Transmission Settings for Maximum Security
In order to make sure that none of the services included in Transmission are going to leak your IP address, I recommend to set the following settings. These recommendations are based on discussions of various forums. While disabling these settings might somewhat reduce the number of peers you can connect to, it is better to keep them disabled to minimize the chance of leaking your IP (if you are using a private tracker, you should disable these options anyway).
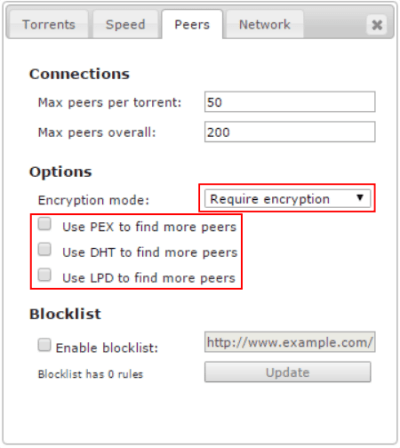
In Transmission Web UI go to Settings and Peer tab.
Set Encryption mode to Require encryption, and uncheck PEX, DHT and LPD
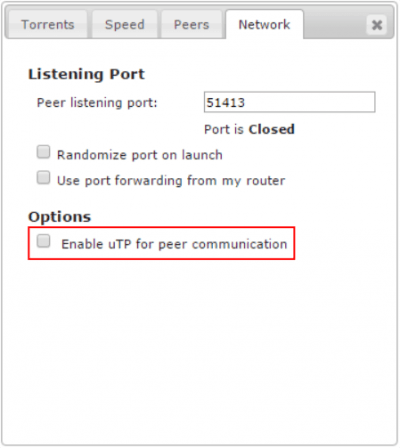
In the Network tab, the Peer listening port is closed, which will limit the number of available peers you can connect to, but opening the port over VPN is not recommended as it greatly reduces security. Some VPN providers offer port forwarding like PIA do, but it requires additional configuration and it is better to avoid opening ports in terms of security. However, for private trackers an open port might be required, stay tuned for a guide for port forwarding with PIA and VPN Split Tunnel.
Make sure Enable uTP for peer communication is disabled.
Confirm Transmission is Using VPN Split Tunnel
We want to make sure that Transmission is using the VPN tunnel. A great way to do this is to download a torrent file from TorGuard. They have a great service called Check My Torrent IP Address. To download the torrent file click on
Alternatively, you can Save Link Location in Firefox or Copy link address in Chrome and copy directly into Transmission's enter URL field.
Note: the “Tracker returned an error message” is normal. The important part is the IP address at the end of the line. It should be the VPN server's IP address.
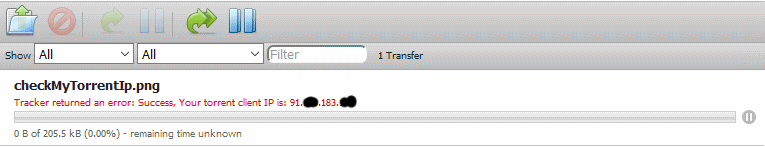
You can copy the IP address and check with IP Tracker. Just paste the IP address and the result should show you the location. Make sure it matches the VPN server's location you use (in our case it is Sweden).
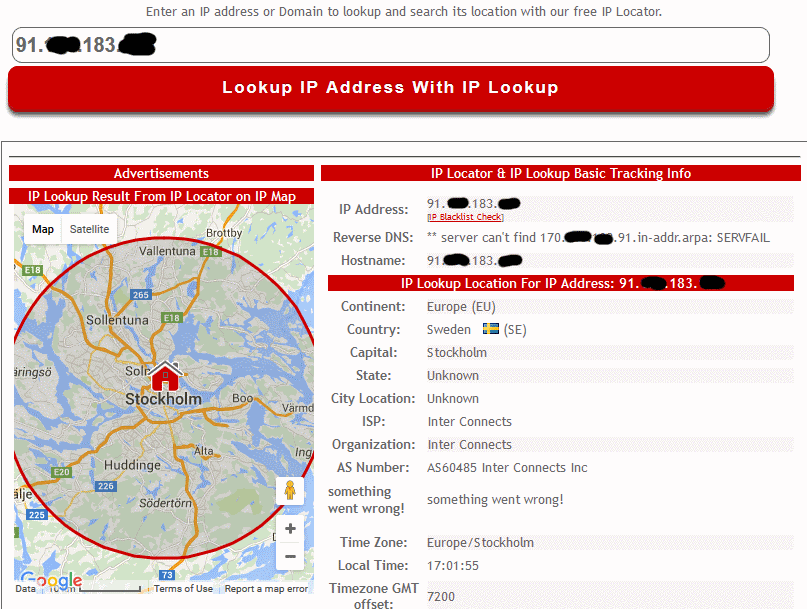
If the IP Lookup matches the VPN server's location, you successfully configured Transmission for VPN Split Tunneling.
Resolve Permission Issues
In Part 1 the VPN Split Tunnel guide we recommended to add your regular user to the vpn group, and to add vpn user to your regular user's group. It is important to avoid any permission related issues with the downloaded torrents. We configured Transmission's permissions for downloaded torrents to be fully accessible (read, write, execute) by vpn user and members of the vpn group.
If you use automation software like Sonarr or CouchPotato, the user who is running these services should be added to the vpn group. If you run the automation software as your regular user then you should not need to make any further changes to permissions beyond what you did in Part 1.
sudo usermod -aG vpn user-running-automation